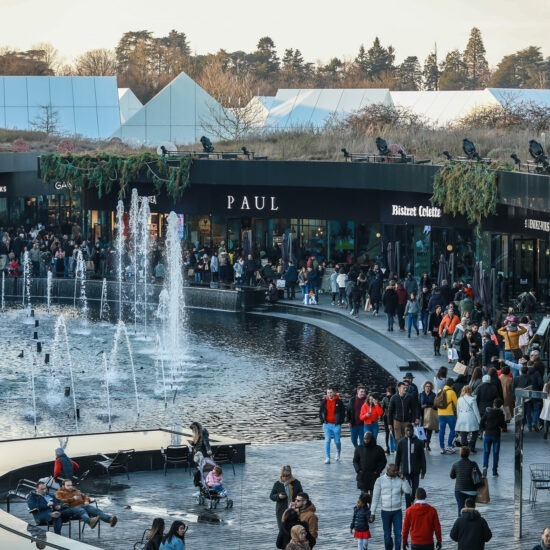WISHIBAM
La plateforme omnicanale pensée terrain
Dans un monde où la personnalisation de l’expérience client est clef, la plateforme omnicanale Wishibam est bien plus qu’un simple logiciel SaaS. Nous sommes le partenaire de référence des outlets, des centres commerciaux, des retailers et des collectivités locales lorsqu’il s’agit de digitaliser leurs activités B2C ou B2B efficacement. Notre technologie tient compte de votre réalité opérationnelle pour une expérience utilisateur sur-mesure qui répond à vos enjeux de croissance.

0+
années d'expérience dans la tech et le retail
Vos clients ont changé, adaptez-vous !
Le commerce unifié vous permet de répondre efficacement aux enjeux de votre client physique comme digital qui veut une expérience d'achat exceptionnelle sur tous les canaux. Nous mettons le meilleur de la technologie pour supprimer les pain points de votre activité et vous permettre de renouer avec une croissance durable. Notre business model est construit de telle sorte que votre réussite est la notre. Notre équipe peut vous accompagner sur toutes les phases de votre projet.
Conseil en transformation digitale
Notre équipe vous aide à définir et à mettre en place la stratégie digitale qui fonctionnera chez nous. Remettre en question vos certitudes pour clarifier vos besoins et vos enjeux, définir votre roadmap et la timer notre expertise retail se mêle à notre expertise digitale pour cocréer ce que sera votre transformation numérique.
Intégration Technique
Notre plateforme omnicanale modulaire est robuste et vous accompagnera dans votre croissance. Basée sur des APIs, nous nous connectons rapidement à votre écosystème existant.
Accompagnement Marketing
Notre plateforme omnicanale a été pensée pour s'indexer parfaitement sur les moteurs de recherche. Notre équipe marketing travaille main dans la main avec notre équipe produit pour que notre e-commerce réponde à toutes les attentes des moteurs de recherche. Notre réussite c'est votre réussite, notre équipe d'acquisition client pourra vous accompagner sur les sujets SEOs comme SEM sans frais de démarrage ni budget minimum.
Délégation opérationnelle
Votre équipe digitale n'est pas encore complète ? Nous pouvons vous accompagner dans le recrutement des profils dont vous aurez besoin pour réussir. Vous souhaitez externaliser cette activité ? Nous gérons aussi pour compte de tiers !









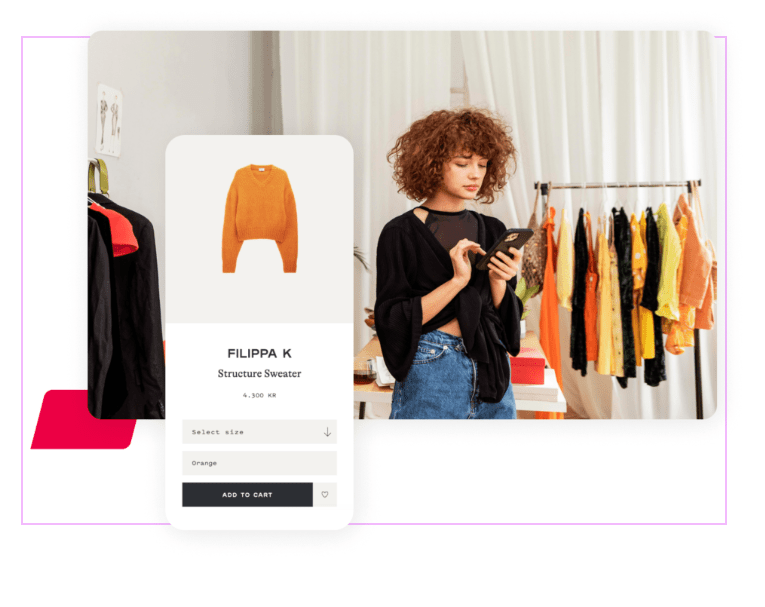
La plateforme omnicanale pensée pour les retailers
- E-commerce front personnalisé
- Retraitez et enrichissez votre Donnée avec notre hub d'intégration
- Elargissez votre catalogue produit avec notre Marketplace
- Gérez intelligemment votre logistique avec notre OMS omnicanal
- Suivez vos performances de façon consolidé avec nos data board
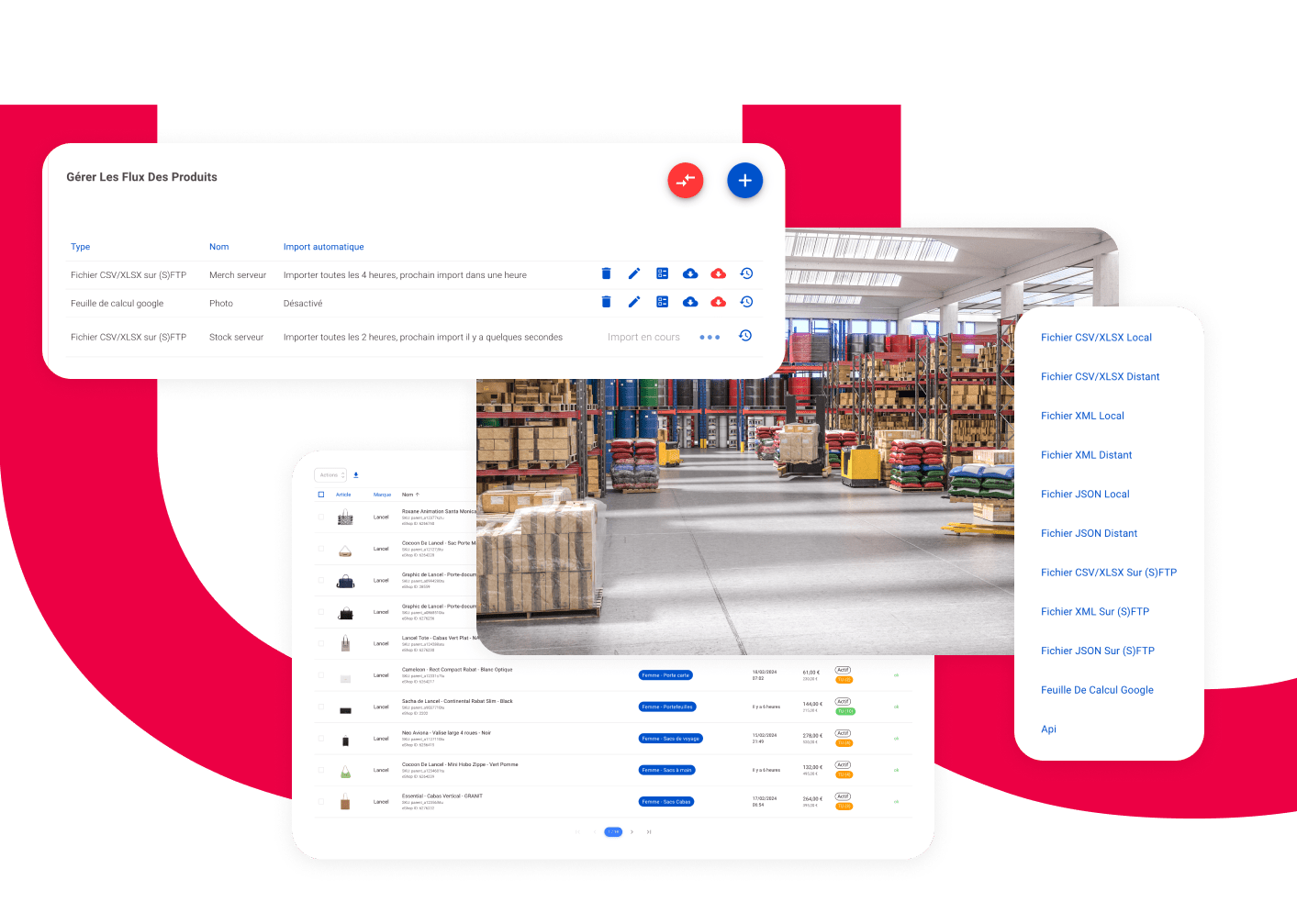
Storefronts
Flux produit
Marketplace
OMS omnicanal
0+
Projets déployés
0+
Marques partenaires
0
Pays
0+
Wishibamiens
Cas clients
Ce qu'ils pensent de nous

Renaud Maret

Dominique Gazeau